Shadow payroll automation: Where do you sit on the maturity curve?
By now you’ve probably heard of shadow payroll automation – the path to hyper-streamlined and super-efficient shadow payroll processes. In fact, we’ve written about shadow payroll automation before, but we wanted to take this opportunity to share our framework on shadow payroll maturity.
In this article, we’ll step you through the different levels of shadow payroll maturity, help you to understand what each level looks like, and explain what might motivate a company to level-up.
“No longer a new concept, shadow payroll automation is now an accepted strategy and many globally mobile companies are engaged in moving themselves along the path to shadow payroll automation maturity. In many cases, the questions surrounding this decision are no longer whether and when to do it, but how to do it right".
Putting automation to work
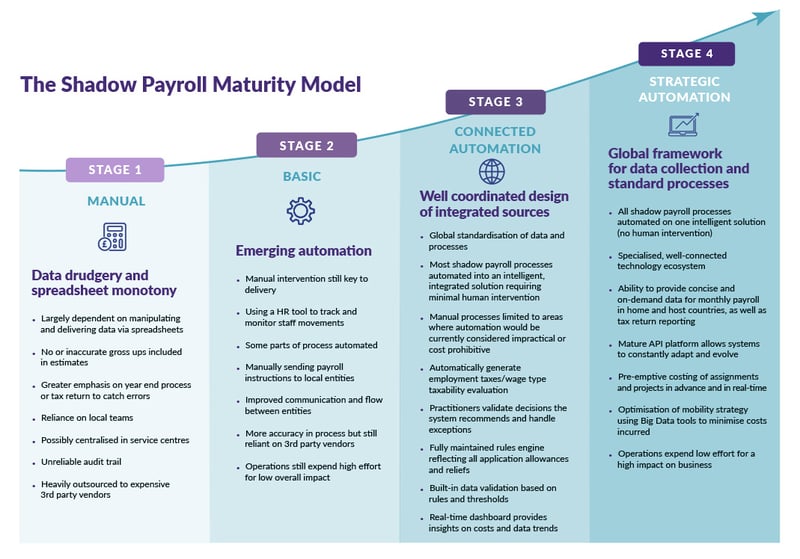
Based on our experience with numerous shadow payroll automation initiatives, Certino has formulated the Shadow Payroll Automation Maturity Model - which is a scale to measure a company’s shadow payroll maturity to help understand the steps that are required to achieve the required automation levels.
There are at least four defined stages. It starts with a manual approach, and as you move up each level it integrates more and more elements of automation.
As companies move up the levels they are able to make huge process efficiencies by minimising low-value added manual tasks, and standardising repeatable processes. As automation across shadow payroll matures, companies soon realise reduced costs, streamlined processes, higher accuracy and greater compliance.
Many shadow payroll processes are currently very high effort with low impact and as you progress through the maturity stages, the effort is minimised and the impact is huge.
The shadow payroll maturity model framework
In this section, we’ll walk you through a deeper dive into shadow payroll automation maturity to help you determine whether you’re ready to talk to an expert about your automation needs or how to do more with the shadow payroll capabilities you already have.
Once you’ve identified your level, you can read more about each maturity stage and uncover key steps to improve your shadow payroll processes. To help guide you, we’ve listed bullet points of the key attributes you might find within each stage. You’ll also discover what’s available to you as your company moves up the curve.
Each stage of maturity unlocks even more benefits, significantly reducing time and costs, all while simplifying the once highly complex and manual processes.
The four levels of shadow payroll automation
The journey to strategic automation for most companies begins with a combination of existing manual processes and some integrated automation.
From there, companies follow a progression from basic automation to connected automation until finally achieving strategic automation.
“The shadow payroll automation maturity model isn’t a roadmap that’s intended to lead everyone towards strategic automation. Yet, many companies could benefit greatly from increased automation, which is why it’s important for Global Mobility leaders to understand what’s possible."
Stage One: Manual
Data drudgery and spreadsheet monotony
Most shadow payroll processes start with a web of shared documents and spreadsheets.
This is labour-intensive data collection and data cleansing with a person sitting at a desk pulling data from multiple data sources, sometimes including payslips in PDF format. The entire process is likely to be non-systematic (i.e., calculations for one country are done based on ad-hoc requests). This process relies on each separate entity to provide their data timely and accurately, and often, awaits data from third party providers e.g. relocation companies.
While manual processes are quick to set up, and initially very cheap, with no development projects to worry about – as the company grows, the information becomes more complex, and the risk of error (and extra costs) skyrockets. Many times, we find there’s no tax and social security gross ups included in payroll estimates, and no advance planning for tax reliefs. Efforts are frequently centralised in service centres with many man hours spent with little oversight from a tax specialist, either internally or externally.
These standard and manual processes are open to human error, and mistakes can lead to late filings, and large underpayments or overpayments at year-end. Plus, there is likely duplicate data collection and aggregation work (i.e. higher cost) when it comes to tax return filing.
With complex expatriate rules changing from country-to-country, the process starts to become increasingly complex and opaque. Yet today, the next level of shadow payroll automation is more accessible than ever before.
Stage Two: Basic
Emerging automation
At this basic level of maturity, automation is not typically a planned activity but happens in pockets across teams at different levels. Some steps within the shadow payroll process may contain a certain level of system automation although often in a siloed and non-consistent manner. This often means manual intervention is still key to successful delivery.
The result is a patchwork quilt of different shadow payroll approaches stitched together by manual work. While some parts of the process will be automated such as core compensation data collection, there may still be issues with local entity buy-in.
Most basic approaches will likely have correctly identified those with a shadow payroll requirement using HR tools to track and monitor staff movements. You may be able to pull data from general ledgers, and while not entirely accurate, this is better than estimated or no reporting. This, in turn, along with some automation means there is better communication across entities of the compliance needs and reporting requirements.
However, compensation collection remains one of the biggest headaches to your shadow payroll processes, even if there’s some automation, given the amount of different data sources. Data collection tools may also be a third party solution not integrated into your current systems. Due to many factors, costs, bandwidth, resistance, this may have to be a hybrid approach between countries with some automation and a necessity to use spreadsheets, especially in the countries with less outbound employees.
On top of that, basic approaches are often still manually sending payroll instructions to local entities and relying on them to file and pay correct amounts which do not consider all available reliefs and/or not all income is reported correctly.
Most global mobility teams are operating at this level of automation, but many could benefit from adding a layer of shadow payroll automation.
Stage three: Connected automation
Well coordinated design of integrated sources
Here all shadow payroll processes are automated on one intelligent solution with minimal human intervention. The entire shadow payroll process is automated from end-to-end to automatically generate employment taxes and/or wage type taxability evaluation. This will involve some API integration with existing systems and payrolls and possibly, external tools and provider reports e.g. your relocation provider, travel tracker tools or payroll vendors.
Of course, there will be some entities outside of or only partially in the process due to numbers involved or the IT bandwidth in that country, but the intention would be to maximise the automation opportunities.
From accurate and timely host country reporting and remittance to general ledger journal entries and annual shadow payroll reports - the entire process is fully connected. In addition, reporting in the home location especially for social security can be achieved. This leaves practitioners only needing to check and validate the decisions the system recommends for the vast majority of cases.
At this stage, companies are able to manage shadow payroll globally and in each location in hours or days, not weeks or months. A fully maintained rules engine reflects all application allowances and reliefs. Plus, built-in data validation based on rules with standard data input allows the flexibility to configure the reportable compensation, and enables batch calculations at scale, including gross-ups of tax and social security where necessary.
Consolidating data and vendors to a single global process brings efficiency and reduced costs – and allows more visibility into what’s happening in each country and globally. Real time dashboards will allow global mobility departments to assess costs, manage inter-company billing and communicate more effectively with the business lines.
Stage four: Strategic automation
Global standardisation of data and processes
Strategic automation is the right move for large companies that have hundreds of globally mobile employees. At this stage we’re looking at a global standardisation of data and processes within a well-connected technology ecosystem.
At this level of maturity, automation is no longer an add-on to an existing system of processes; fundamentally, systems are designed to adapt to changes. They are data-driven, have the ability to predict changes, and are capable of adapting to them.
Automation is no more an initiative but it becomes the way of life for shadow payroll workflows. Automation is woven into every tax return or budgeting exercise at a global level.
With this strong baseline of automated data, companies can provide concise and on-demand data for monthly payroll reporting in home and host countries, as well as for tax return reporting. Rather than labour intensive work, real-time dashboards provide meaningful insights on a monthly and annual basis – on costs and data trends allowing businesses to use this data in strategic decision making.
Mature API integrations allow systems to constantly evolve and adapt to changes in business needs. This means new services can be quickly delivered with minimal development effort. For example, it allows pre-emptive costing of assignments and projects in advance and in real-time, as well as proactive optimisation of a company’s mobility strategy. At this point, the shadow payroll process required the least effort possible, but the impact on business overall is huge.
To achieve this level of maturity, the automation is guided by experts in shadow payroll automation, who have technical expertise in shadow payroll. A roadmap is established to achieve the set goals as they evolve; this will not only help in adopting technologies, but also transform the way in which systems support the business and processes. It should be noted that what a strategic automation approach would look like for a company will vary greatly by company. That’s why we always advocate a bespoke approach.
The road ahead for automated shadow payroll
It’s easy to look at the sheer scale of what you’re trying to achieve and not know where to start. We recommend mapping out a bespoke roadmap taking planned steps towards the end goal.
Rather than developing a “one size fits all” model, we recommend starting by understanding your current level of maturity and developing a roadmap appropriate for your company.
Success, even at the more basic levels, will strengthen the case for more integrated levels of automation with your current tools and systems and help propel your company’s shadow payroll workstream up the maturity curve.
The role of the global mobility department is elevated. Rather than being perceived as a cost centre, (especially if service centres and dedicated teams are used), with ever-increasing overheads as the amount of information and complexity increases – runs smoothly and efficiently saving on costly processes and man hours.
Accurate and timely payroll may also help cash flow by reducing overpayments of tax and also reduces risk of audit and review by the tax authorities.
This allows teams to concentrate on more value-added work and concentration on the complex cases, rather than the manual screen work that was necessary to handle shadow payroll using pre-automated processes.
In summary
The shadow payroll automation maturity model provides an objective way to assess where a company is and where it can get to, with respect to shadow payroll automation. What’s important is finding the right level of automation to help you meet your organisation’s near-term and long-term needs.
With the ever growing need for efficiency and ready access to technologies, shadow payroll automation has become a business imperative to adopt. The investment in automation technology can directly impact the bottom line by saving on tax overpayments, cutting human capital costs, and reducing unintended human errors.
With the right specialist support and making the most of the technology you’ve already got through API integrations, you can quickly begin to see results by bringing all your data together into one view. When selecting an intelligent automation platform, factoring in global capability, and ease of integration is critical.
Ultimately, intelligent shadow payroll automation is going to bridge the gaps between human and computer-based processes – augmenting and transforming, as opposed to pure replacement.
As with any new competency, selecting a platform and establishing a sustainable practice can be daunting without the right partner to ensure frictionless implementation. As shadow payroll experts, Certino recognises the importance of shadow payroll process automation and is excited to partner with you on this journey.
How does your business benchmark?
Contact us to get started with a shadow payroll maturity assessment – or download the Guide to shadow payroll maturity PDF here.